codeable_models.CClass¶
-
class
codeable_models.CClass(metaclass, name=None, **kwargs)¶ CClassis used to define classes. Classes in Codeable Models are instances of metaclasses (defined usingCMetaclass).Superclasses:
CClassifier- Parameters
metaclass (CMetaclass) – The meta-class this class is instantiated from. Each class requires a meta-class, defined using
CMetaclass.name (str) – An optional name.
**kwargs –
Pass in any kwargs acceptable to superclasses. In addition,
CClassaccepts:stereotype_instances,values,tagged_values.stereotype_instances:Any
CStereotypeextending the meta-class of this class can be defined on the class as a stereotype instance. That is, the list of stereotypes on the meta-class defines the possible stereotypes instances of the class. The kwarg accepts a list of stereotype instances or a single stereotype instance as argument.
values:Just as objects can define
valuesfor attributes defined on their classes, a class can define values for any attribute defined on their meta-class. They can be used via the interface ofCClass. Internally, a so-called class object (explained below) is used to store and manage those values.valuesaccepts a dict of key/value pairs. The value types must conform to the types defined for the attributes.
tagged_values:Any attribute on a
CStereotypeextending the meta-class of this class, which is also a stereotype instance of this class, can be set as a tagged value on this class. The keyword argtagged_valuescan be used to set them just like ordinary attribute values.tagged_valuesaccepts a dict of key/value pairs. The value types must conform to the types defined for the attributes.
Examples:
An example class definition is:
cloud = CClass(execution_environment, "Cloud")
Here is a class that defines a stereotype instance (assuming the meta-class is extended by this stereotype):
cloud = CClass(execution_environment, "Cloud", stereotype_instances = cloud_env_type)
Main Relations:
The main relations of
CClassare shown in the figure below.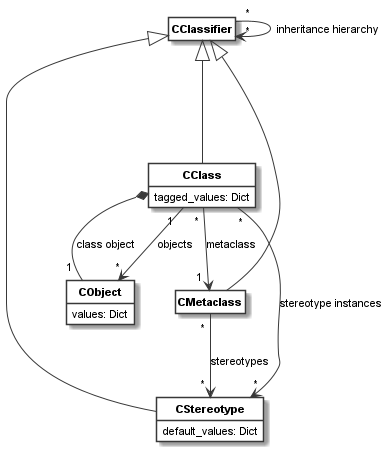
As can be seen, each
CClassis aCClassifierand has aCMetaclass. It has instances of typeCObject.CClassuses a special object, the class object, to manage its instance relation to its meta-class. That is, classes offerCObjectcapabilities such as attribute values and links via the class object. For most purposes, the class object is hidden byCClass, i.e. the class object is usually not used by the user directly.Each class can have stereotype instances of the stereotypes defined on its meta-class.
-
add_links(links, **kwargs)¶ Add links on this class (which are based on associations defined on the class’ meta-class). Uses the function
add_links(). That is, it is possible to use the following equivalently:add_links({<this_class>: <links>}, <**kwargs>)
- Parameters
links – The new links to be defined.
**kwargs – Any keyword arg acceptable to
add_links().
- Returns
List of created link objects.
- Return type
list[CLink]
-
property
all_objects¶ Getter to get all instances of this class, defined directly on the class and on any sub-class.
- Type
list[CObject]
-
association(target, descriptor=None, **kwargs)¶ Method used to create associations on this class. See documentation of method
associationonCClassifierfor details.- Parameters
target – The association target classifier.
descriptor – An optional descriptor making it easier to define associations with a simple string.
**kwargs – Accepts all keyword arguments acceptable to
CAssociationto define associations.
- Returns
The created association.
- Return type
-
delete()¶ Delete the class. Also deletes all direct instances of the class. Remove the class from stereotype instance relations. Removes it from its meta-class relation. Deletes the class object. Calls
delete()on superclass.- Returns
None
-
delete_links(links, **kwargs)¶ Delete links on this class (which are based on associations defined on the class’ meta-class). Uses the function
delete_links(). That is, it is possible to use the following equivalently:delete_links({<this_class>: <links>}, <**kwargs>)
- Parameters
links – The links to be deleted.
**kwargs – Any keyword arg acceptable to
delete_links().
- Returns
List of deleted link objects.
- Return type
list[CLink]
-
delete_tagged_value(name, stereotype=None)¶ Delete tagged value of a stereotype attribute with the given
name. Optionally the stereotype to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its stereotype.- Parameters
name – The name of the attribute.
stereotype – The optional stereotype on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
Value of the attribute.
- Return type
Supported Attribute Types
-
delete_value(attribute_name, classifier=None)¶ Delete the value of an attribute with the given
attribute_name. Optionally the classifier to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its classifier.- Parameters
attribute_name – The name of the attribute.
classifier – The optional classifier on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
Value of the attribute.
- Return type
Supported Attribute Types
-
get_linked(**kwargs)¶ Method to get the linked classes defined for this class filtered using criteria specified in kwargs.
- Parameters
**kwargs –
Defines filter criteria.
association:Include links only if they are based on the specified association.
role_name:Include links only if they are based on an associations having the specified role name either as a target or source role name.
- Returns
List of linked classes
- Return type
list[CClass]
-
get_links_for_association(association)¶ Method to get all link objects which are defined based on the given association.
- Parameters
association – Association used to filter the links.
- Returns
The list of link objects.
- Return type
list[CLink]
-
get_object(name)¶ Returns an object with the given name with is instance of this classifier, or if not present
None. If multiple objects are found, the first found object is returned.- Parameters
name – The object name to search for
- Returns
An object with the given name or None.
- Return type
-
get_objects(name)¶ Returns all objects with a given name with are instances of this classifier.
- Parameters
name – The object name to search for
- Returns
The objects with the given name.
- Return type
list[CObject]
-
get_tagged_value(name, stereotype=None)¶ Get the tagged value of a stereotype attribute with the given
name. Optionally the stereotype to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its stereotype.- Parameters
name – The name of the attribute.
stereotype – The optional stereotype on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
Value of the attribute.
- Return type
Supported Attribute Types
-
get_value(attribute_name, classifier=None)¶ Get the value of an attribute with the given
attribute_name. Optionally the classifier to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its classifier.- Parameters
attribute_name – The name of the attribute.
classifier – The optional classifier on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
Value of the attribute.
- Return type
Supported Attribute Types
-
instance_of(classifier)¶ Returns
Trueif this class is instance of theclassifier, elseFalse.- Parameters
classifier – A classifier to check against.
- Returns
Boolean result of the test.
- Return type
bool
-
property
links¶ Getter for getting the links defined for this class. Class links are based on the associations defined for the class’ meta-class.
- Type
list[CLink]
-
property
metaclass¶ Getter and setter to get the meta-class of this class.
- Type
-
set_tagged_value(name, value, stereotype=None)¶ Set the tagged value of a stereotype attribute with the given
nametovalue. Optionally the stereotype to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its stereotype.- Parameters
name – The name of the attribute.
value – The new value.
stereotype – The optional stereotype on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
None
-
set_value(attribute_name, value, classifier=None)¶ Set the value of an attribute with the given
attribute_nametovalue. Optionally the classifier to consider can be specified. This is needed, if one or more attributes of the same name are defined on the inheritance hierarchy. Then a shadowed attribute can be accessed by specifying its classifier.- Parameters
attribute_name – The name of the attribute.
value – The new value.
classifier – The optional classifier on which the attribute is defined.
- Returns
None
-
property
stereotype_instances¶ Getter to get and setter to set the stereotype instances of this class.
The stereotype instances must be stereotypes extending the meta-class of the class.
The setter takes a list of stereotype instances or a single stereotype instance as argument. The getter always returns a list.
- Type
list[CStereotype]|CStereotype
-
property
tagged_values¶ Getter for getting all tagged values of the class using a dict, and setter of setting all tagged values of the class based on a dict. The dict uses key/value pairs. The value types must conform to the types defined for the attributes.
- Type
dict[str, value]
-
property
values¶ Getter for getting all values of the object using a dict, and setter of setting all values of the object based on a dict. The dict uses key/value pairs. The value types must conform to the types defined for the attributes.
- Type
dict[str, value]